- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
Účinky křemičitého prášku na trvanlivost
2021-07-13
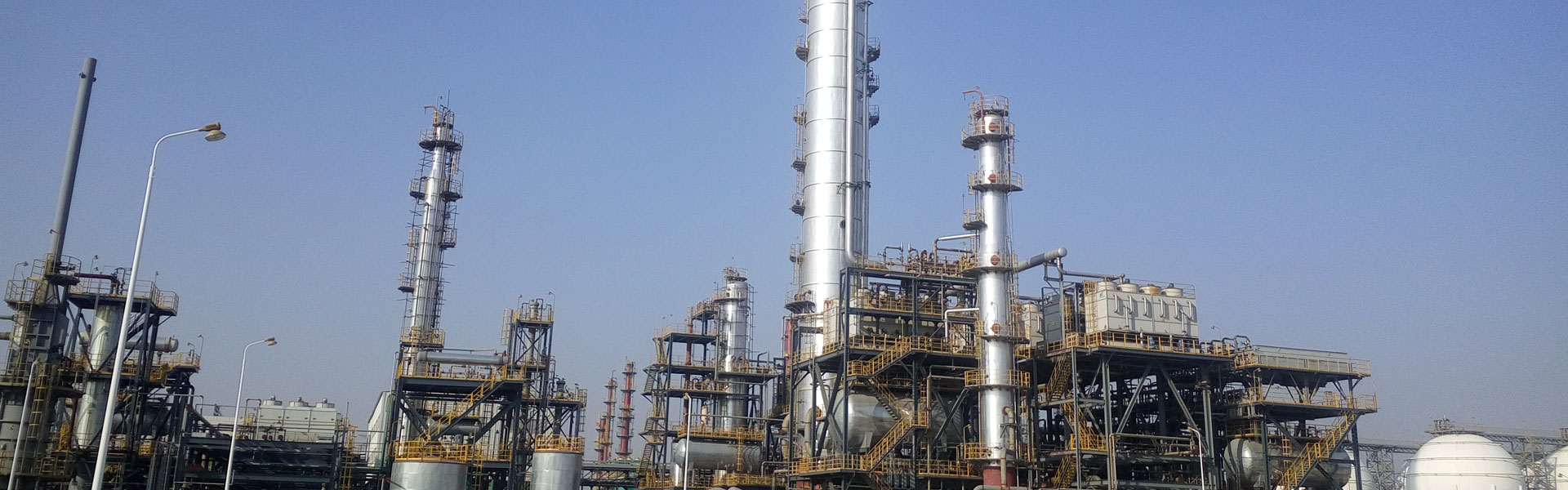
Trvanlivost betonu zahrnuje mrazuvzdornost, nepropustnost, chemickou odolnost, odolnost oceli proti korozi a erozi. Budu mluvit jen o jeho mrazuvzdornosti, nepropustnosti a chemické odolnosti vůči betonu. Erozivní účinek.
a) Mrazuvzdornost: Když množstvíKřemičitý prášekje malý, mrazuvzdornost křemičitého kouřobetonu je v zásadě stejná jako u běžného betonu. Když množství křemičitého prášku přesáhne 15%, je jeho mrazuvzdornost špatná. Prostřednictvím velkého počtu testů byl tento pohled v zásadě potvrzen. Hlavním důvodem je, že když kouřový dým překročí 15%, roztažnost betonu se zvýší, relativní dynamický modul pružnosti se sníží a pevnost v tlaku prudce klesne. Z hlediska vnitřních charakteristik betonu je specifický povrch malý a koeficient rozteče je velký.
b) Impermeability: Because Křemičitý prášek particles are small, 20-100 times smaller than cement particles, they can be filled into the voids between cement particles to make concrete compact. At the same time, the secondary hydration of silica powder blocks new products. Permeation channels in concrete, so the impermeability of silica fume concrete is very strong, the permeability of concrete increases with the increase of water-binder ratio, this is because the compactness of water-cement is relatively poorer than that of concrete.
c) Chemical resistance: Mixing Křemičitý prášek into concrete can reduce the content of Ca (OH) 2 and increase the compactness of concrete. It can effectively improve the corrosion ability of weak acid. However, it cannot be used in strong acid or high-depth weak acid. CSH decomposes in acid. In addition, it is also resistant to salt corrosion, especially to chlorides and sulfates. The reason why it is resistant to salt corrosion is that the silica fume concrete is denser and the pore structure is improved, thereby reducing The transmission speed of harmful ions is reduced and the formation of soluble Ca (OH) 2 and ettringite (3CaO·Al2O3·3CaSO4 ·32H2) is reduced, and the result of increasing hydrated calcium silicate crystals.
a) Mrazuvzdornost: Když množstvíKřemičitý prášekje malý, mrazuvzdornost křemičitého kouřobetonu je v zásadě stejná jako u běžného betonu. Když množství křemičitého prášku přesáhne 15%, je jeho mrazuvzdornost špatná. Prostřednictvím velkého počtu testů byl tento pohled v zásadě potvrzen. Hlavním důvodem je, že když kouřový dým překročí 15%, roztažnost betonu se zvýší, relativní dynamický modul pružnosti se sníží a pevnost v tlaku prudce klesne. Z hlediska vnitřních charakteristik betonu je specifický povrch malý a koeficient rozteče je velký.
b) Impermeability: Because Křemičitý prášek particles are small, 20-100 times smaller than cement particles, they can be filled into the voids between cement particles to make concrete compact. At the same time, the secondary hydration of silica powder blocks new products. Permeation channels in concrete, so the impermeability of silica fume concrete is very strong, the permeability of concrete increases with the increase of water-binder ratio, this is because the compactness of water-cement is relatively poorer than that of concrete.
c) Chemical resistance: Mixing Křemičitý prášek into concrete can reduce the content of Ca (OH) 2 and increase the compactness of concrete. It can effectively improve the corrosion ability of weak acid. However, it cannot be used in strong acid or high-depth weak acid. CSH decomposes in acid. In addition, it is also resistant to salt corrosion, especially to chlorides and sulfates. The reason why it is resistant to salt corrosion is that the silica fume concrete is denser and the pore structure is improved, thereby reducing The transmission speed of harmful ions is reduced and the formation of soluble Ca (OH) 2 and ettringite (3CaO·Al2O3·3CaSO4 ·32H2) is reduced, and the result of increasing hydrated calcium silicate crystals.
Předchozí:Toxicita polyetherpolyolu při skladování